Find Your Perfect Home
Explore our diverse selection of rental properties.
Find Your Perfect Home
Explore our diverse selection of rental properties.
What Makes Our Properties Unique:
Prime Locations: Our properties are strategically located in desirable neighborhoods with easy access to amenities, transportation, and entertainment.
Exceptional Maintenance: We prioritize the upkeep of our properties, ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable living experience for all residents.
Resident-Focused Services: We offer a range of resident-focused services, including 24/7 emergency maintenance, online portals for convenient rent payments and maintenance requests, and a dedicated team to address any concerns.
What Makes Our Properties Unique:
Prime Locations: Our properties are strategically located in desirable neighborhoods with easy access to amenities, transportation, and entertainment.
Exceptional Maintenance: We prioritize the upkeep of our properties, ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable living experience for all residents.
Resident-Focused Services: We offer a range of resident-focused services, including 24/7 emergency maintenance, online portals for convenient rent payments and maintenance requests, and a dedicated team to address any concerns.
Different kind of house
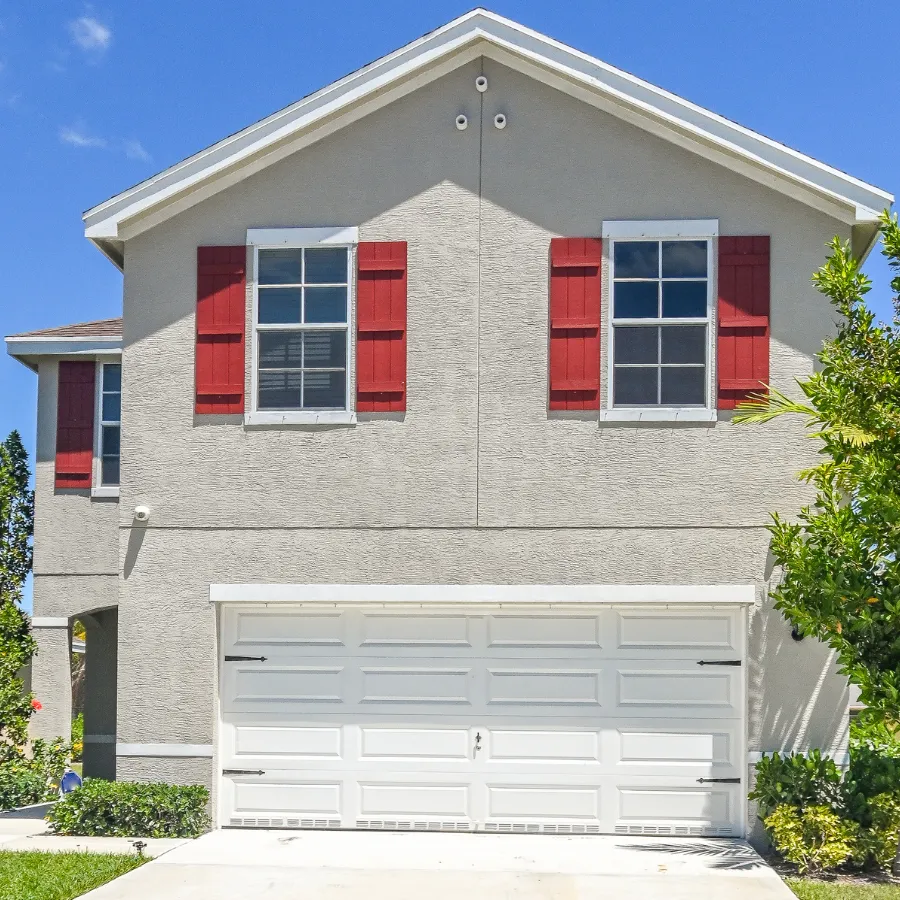

Single-family
A single-family home, as defined by the U.S. Census Bureau, encompasses a broader range of housing types beyond the typical detached house. Key characteristics include separation from adjacent units by a ground-to-roof wall and independent utilities and HVAC systems. This structure affords homeowners greater privacy and autonomy.
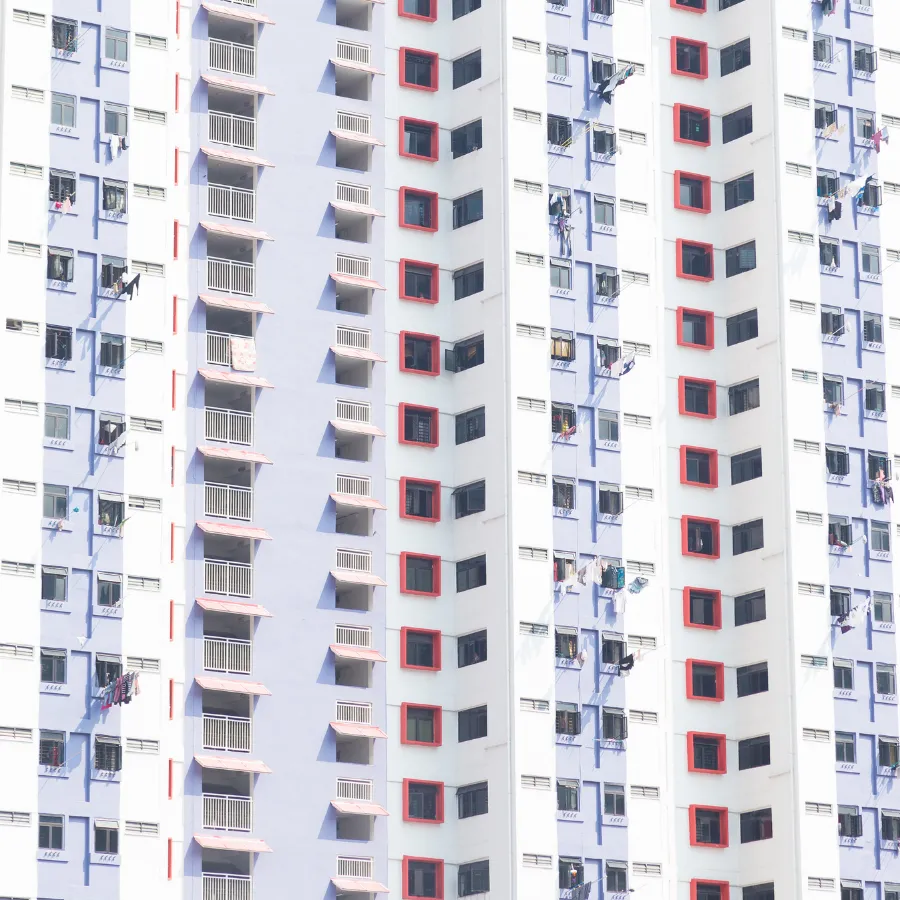

Condo or co-op
Condominiums and cooperatives offer alternative housing options to single-family homes.
Condominiums: You own your individual unit within a building, along with a shared interest in common areas.
Cooperatives: You own shares in a corporation that owns the building, giving you the right to live in a specific unit.
Benefits: Condos and co-ops often offer amenities like gyms or doormen and can be more affordable than single-family homes.
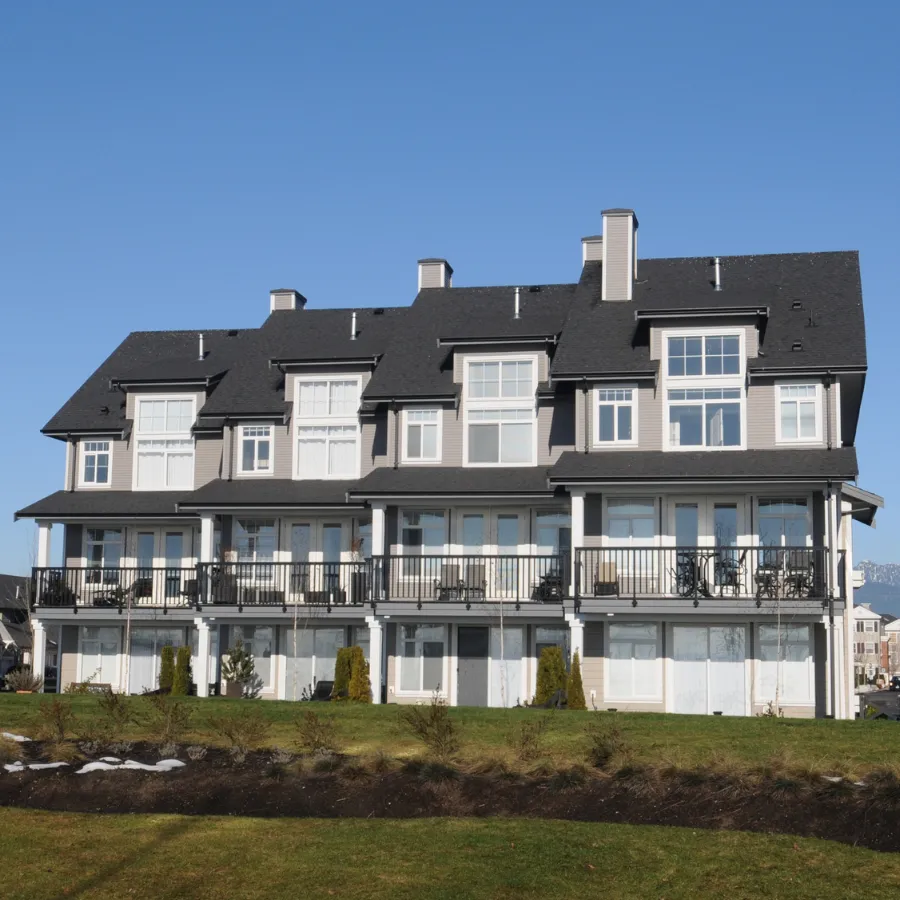

Townhouse
Townhomes are multi-story residences with private entrances that share walls with neighboring units. They generally offer a more affordable option than detached single-family homes in the same area. Potential benefits include shared amenities and outdoor space. However, drawbacks can include limited parking, homeowners association (HOA) fees and rules, and reduced privacy.

Multi-family home
A multi-family home encompasses a range of properties, including duplexes, triplexes, and fourplexes, which accommodate multiple independent living units within a single structure. These properties offer distinct advantages, such as:
* Investment Potential: Generating rental income while residing in one unit.
* Multi-generational Living Arrangements: Providing convenient and comfortable living spaces for family members who may require assistance or prefer independent living within close proximity.

Accessory dwelling unit
An Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) is a versatile housing option that adds a secondary living space to a single-family property. It can be a detached structure or converted from existing space within the home. ADUs offer flexibility, serving as a home for family members or generating rental income. While popular in many areas, ADUs may not be permitted in all locations.
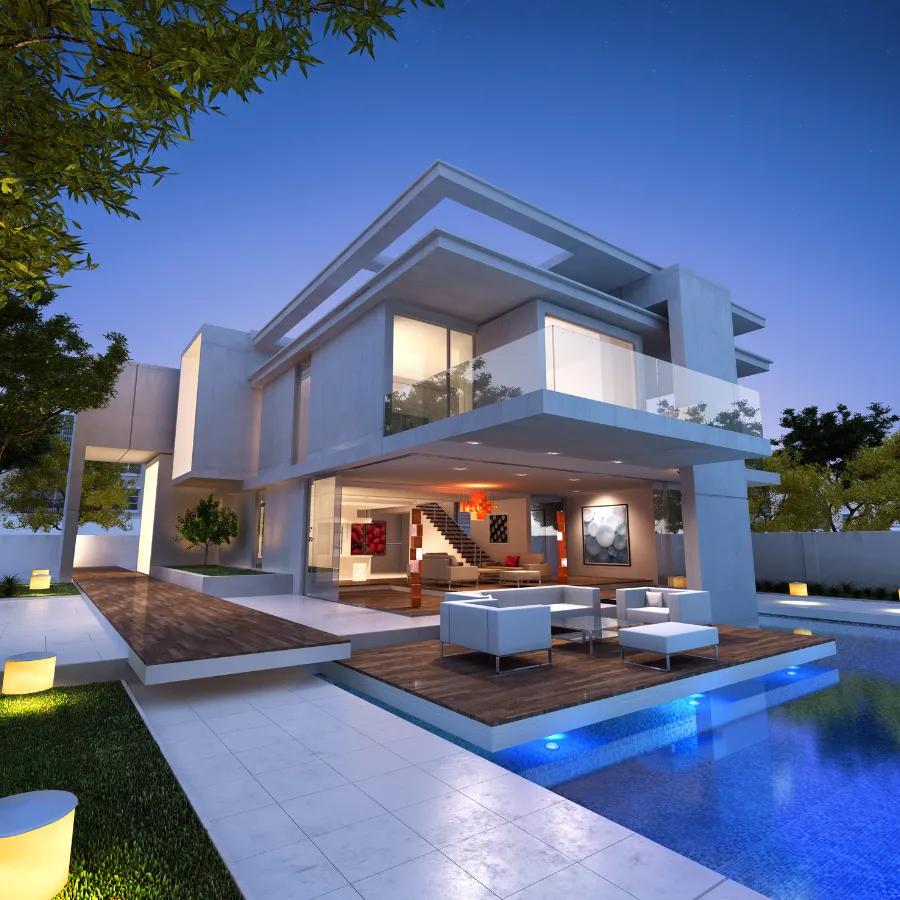

Modular home
Modular homes are factory-built and assembled on-site on a permanent foundation. Unlike mobile homes, which are designed to be moved, modular homes are built to remain in a fixed location.
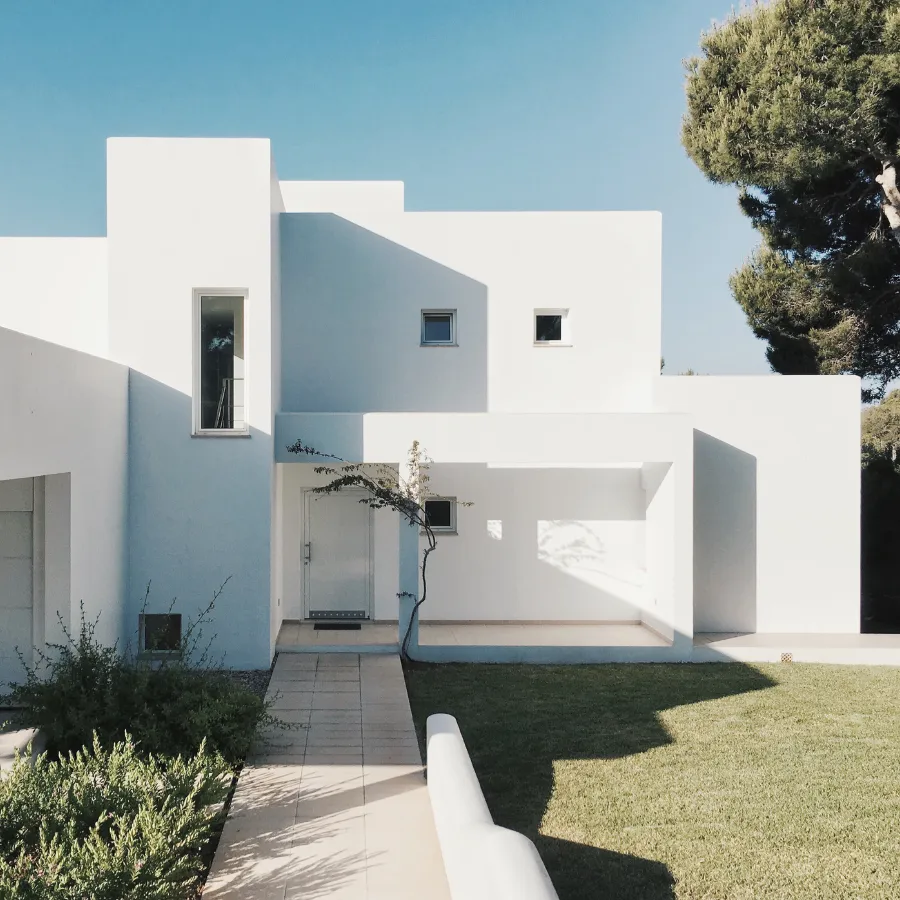

Mobile home
Manufactured homes are constructed in factories and then transported to the desired location. They often offer a more affordable housing option compared to traditional site-built homes. However, financing a manufactured home may have unique considerations.
Additionally, while you may own the home itself, you may need to rent the land on which it sits.
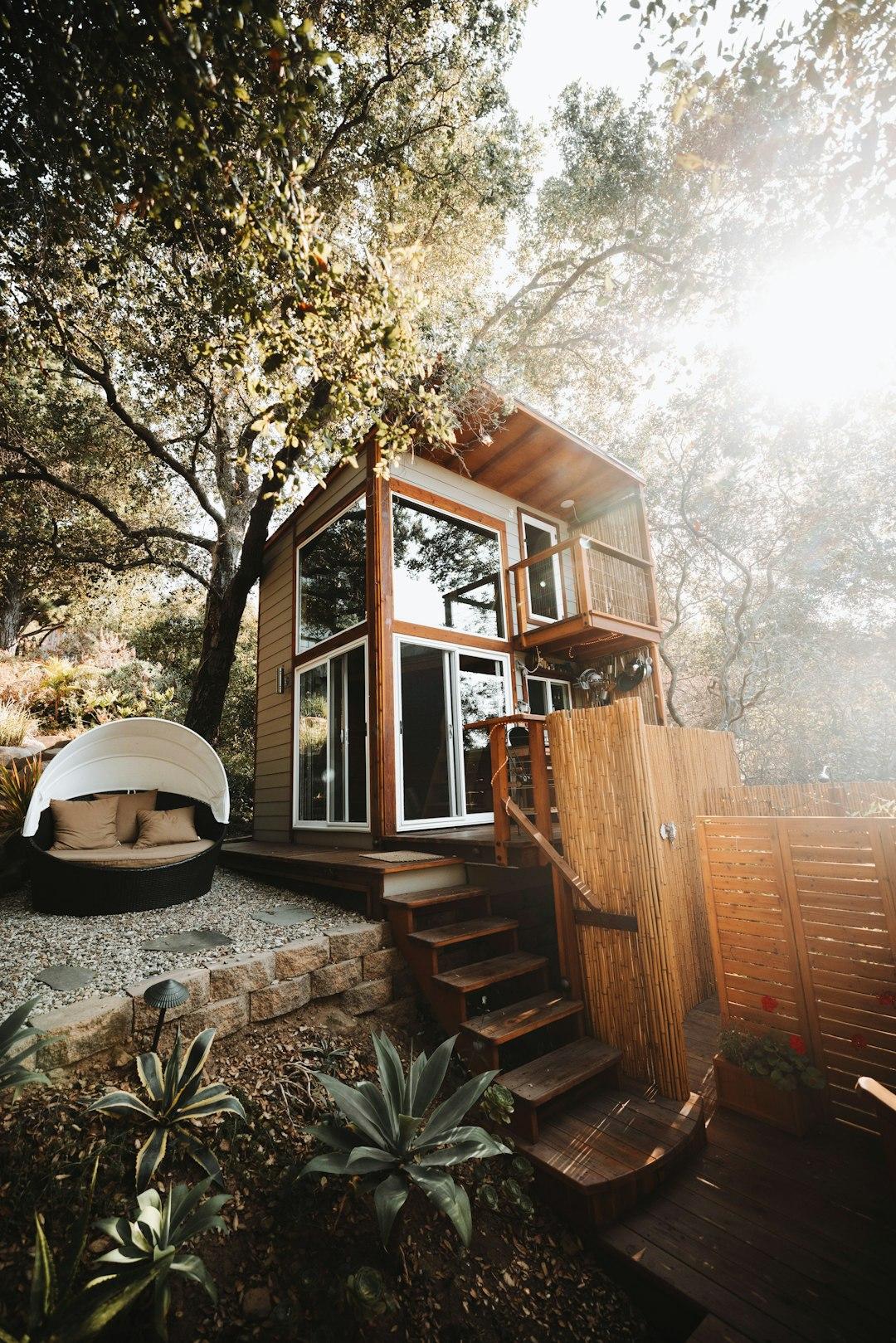

Tiny home or container home
Tiny homes, generally less than 600 square feet, offer an affordable housing option, particularly for first-time homebuyers. Their compact size not only reduces upfront costs but also lowers ongoing expenses for furnishings, heating, and cooling. Container homes, while similar in size, are uniquely constructed from repurposed shipping containers.
Different kind of house

Single-family
A single-family home, as defined by the U.S. Census Bureau, encompasses a broader range of housing types beyond the typical detached house. Key characteristics include separation from adjacent units by a ground-to-roof wall and independent utilities and HVAC systems. This structure affords homeowners greater privacy and autonomy.

Condo or co-op
Condominiums and cooperatives offer alternative housing options to single-family homes.
Condominiums: You own your individual unit within a building, along with a shared interest in common areas.
Cooperatives: You own shares in a corporation that owns the building, giving you the right to live in a specific unit.
Benefits: Condos and co-ops often offer amenities like gyms or doormen and can be more affordable than single-family homes.

Townhouse
Townhomes are multi-story residences with private entrances that share walls with neighboring units. They generally offer a more affordable option than detached single-family homes in the same area. Potential benefits include shared amenities and outdoor space. However, drawbacks can include limited parking, homeowners association (HOA) fees and rules, and reduced privacy.

Multi-family home
A multi-family home encompasses a range of properties, including duplexes, triplexes, and fourplexes, which accommodate multiple independent living units within a single structure.
These properties offer distinct advantages, such as:
* Investment Potential: Generating rental income while residing in one unit.
* Multi-generational Living
Arrangements: Providing convenient and comfortable living spaces for family members who may require assistance or prefer independent living within close proximity.

Accessory dwelling unit
An Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) is a versatile housing option that adds a secondary living space to a single-family property. It can be a detached structure or converted from existing space within the home. ADUs offer flexibility, serving as a home for family members or generating rental income. While popular in many areas, ADUs may not be permitted in all locations.

Modular home
Modular homes are factory-built and assembled on-site on a permanent foundation. Unlike mobile homes, which are designed to be moved, modular homes are built to remain in a fixed location.

Mobile home
Manufactured homes are constructed in factories and then transported to the desired location. They often offer a more affordable housing option compared to traditional site-built homes. However, financing a manufactured home may have unique considerations.
Additionally, while you may own the home itself, you may need to rent the land on which it sits.

Tiny home or container home
Tiny homes, generally less than 600 square feet, offer an affordable housing option, particularly for first-time homebuyers. Their compact size not only reduces upfront costs but also lowers ongoing expenses for furnishings, heating, and cooling. Container homes, while similar in size, are uniquely constructed from repurposed shipping containers.
Don't Just Take Our Word For It



Don't Just Take Our Word For It



1515 N Warson Rd. Suite #133, St. Louis, MO 63132
Copyright © Turn Key Up Investments LLC
CALL US - 636-442-1168
1515 N Warson Rd. Suite #133, St. Louis, MO 63132
Copyright © Turn Key Up Investments LLC
CALL US - 636-442-1168